In This Article
Different Types Of Acne: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments & Prevention
Acne is the most common skin concern prevalent in men and women of all ages. Most commonly seen in teenagers and young adults, due to hormonal fluctuations, acne can also occur during adulthood, especially in women. Acne, whose medical term is acne vulgaris, manifests in different forms, each with a distinct appearance and symptoms. While some types of acne go away on their own, others require proper medical treatment. In this article, let us dive into the different types of acne and their causes and symptoms. Additionally, let us learn about the various treatments to address each type of acne and some preventative measures.
In This Article
Acne Types
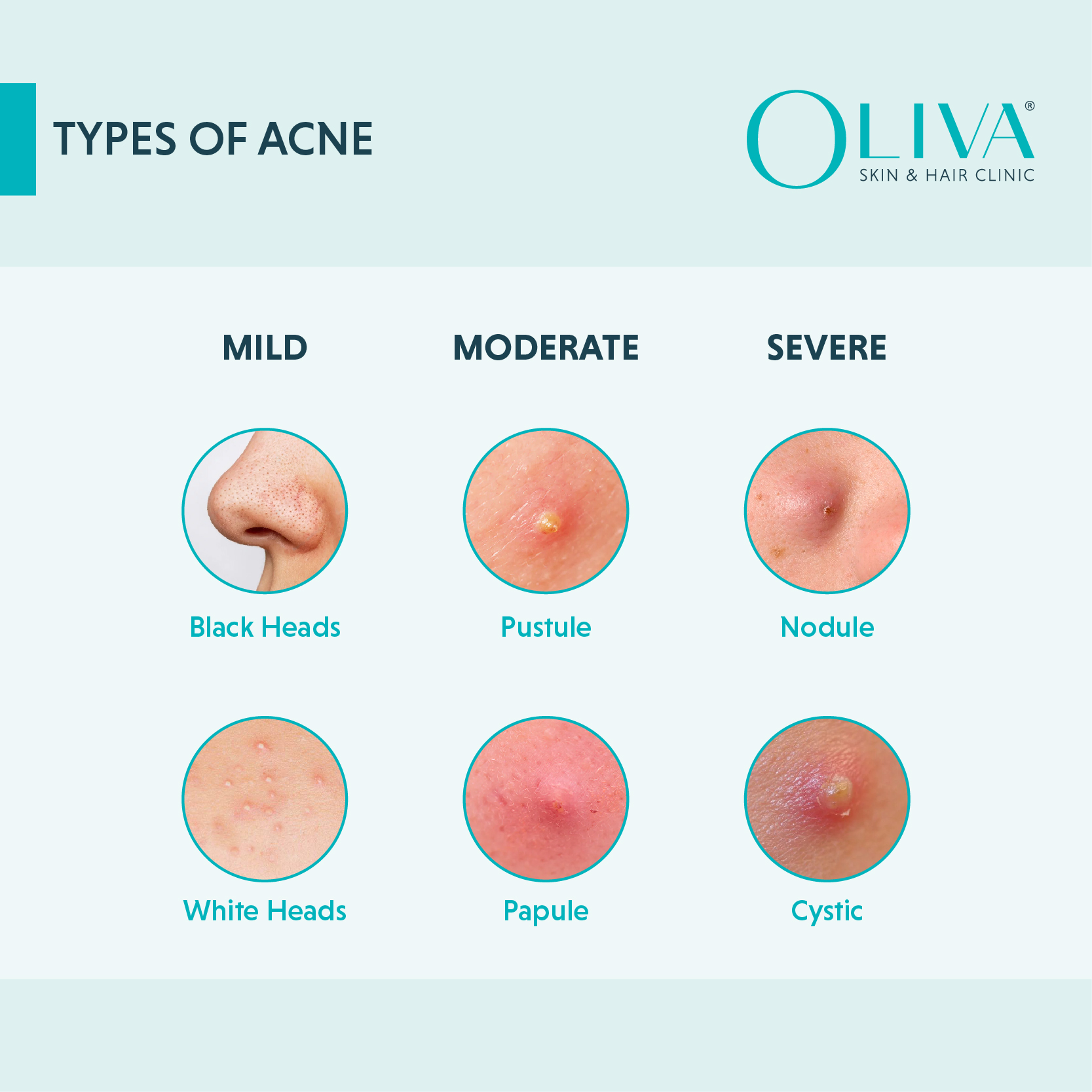
Call it pimples, bumps, breakouts, or blemishes; all talk about acne. But not all are the same. Acne can be present in various forms, from comedones to cysts. When managing these, it is imperative to know what type of acne you are dealing with. Each type requires a different treatment. Identifying the type of acne is the first step to successful treatment, as it helps the dermatologist customise treatments and treat them accordingly. Based on whether inflammatory or non-inflammatory, we can classify acne as below:
- Blackheads
- Whiteheads
- Papules
- Pustules
- Nodules
- Cysts
Let us examine each type of acne in detail, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment and prevention tips.
Blackheads
Blackheads are open comedones that look like tiny black spots on the nose, chin, and forehead. They are a grade-1 type of acne that forms when sebum and dead skin cells clog the skin pores. [1] Blackheads are non-inflammatory, as they do not cause swelling
Causes
Most people assume that the trapped causes the comedones to turn black. It is not. The black hues on the skin surface result from the discolouration of sebum because of air. Possible reasons for blackheads include:
- Excessive sebum or oil production
- Irritated hair follicle
- Hormonal fluctuations
- Harmful skincare products
Symptoms
- Presence of open pores
- Dark or black-coloured bumps
- Having a raised texture
- No associated pain or discomfort
Treatments
Depending on the severity, blackheads are treatable using OTC medications and topical retinoids. The dermatologist may recommend comedone extraction to get rid of them safely. [2]
Prevention
- Clean your face twice a day
- Use non-comedogenic products in your skincare and makeup routine
- Exfoliate gently at least once a week
Whiteheads
Whiteheads are closed comedones under the skin’s surface. These appear as white or flesh-coloured spots on the skin and are grade-1 type of acne. Slightly raised in appearance, they occur mostly on the neck, back, chest, nose, forehead, and chin.
Causes
Whiteheads are a milder type of acne formed due to increased oil production in the hair follicles by the skin’s sebaceous glands. But unlike blackheads, the top closes up, looking like a small white bump protruding from the skin. Whiteheads are also non-inflammatory acne lesions that do not cause pain or discomfort.
Symptoms
- Presence of white or flesh-coloured bumps
- Slightly raised
- Tender to touch
Treatments
Dermatologists prescribe topical retinoids or OTC products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to treat whiteheads and comedone extraction to safely remove them. Depending on the severity, they may also recommend chemical peels and laser skin resurfacing treatments.
Prevention
- Wash your face regularly and moisturise it afterwards
- Use oil-free and non-comedogenic skincare products
- Refrain from squeezing the pimples or touching the skin unnecessarily
Papules
Papules are inflammatory grade-2 acne that resemble red or pink bumps on the skin. They occur on the face, neck, chest, buttocks, shoulders, and back and can be tender to the touch. They may leave behind hyperpigmentation marks on the skin.
Causes
Papules form when the skin pores clog due to the accumulation of excess oil, dead skin cells, oil and dirt. The increased presence of bacteria on the skin also triggers the formation of papules.
Symptoms
- Red bumps
- Painful and tender to touch
- Presence of pus in some cases
- Resemble inflamed whiteheads
- Irritation and itching
Treatments
The dermatologist may suggest chemical peel and laser therapies to treat papules effectively.
Prevention
- Clean your face regularly with a gentle cleanser, but avoid scrubbing
- Use non-comedogenic skincare and makeup products
- Remove your makeup before you sleep
- Refrain from touching your skin unnecessarily
Pustules
Pustules are small bumps filled with pus with a white to yellowish appearance and a red halo. They are moderate to severe acne and can occur on the face, neck, back, shoulders and arms. [3]
Causes
Pustules form due to acne or when the blocked skin pores get infected. Other contributing factors include infections, skin disorders, insect bites, and food allergies.
Symptoms
- Tiny blisters filled with white or yellow pus
- Painful to touch
- Presence of redness and inflammation
Treatments
The dermatologist may prescribe OTC topical drugs to treat pustules caused by acne. Depending on the severity, they may also recommend other medications, antibiotics, chemical peels, and light therapy.
Prevention
- Wash the skin always to keep it oil-free
- Use only non-comedogenic products to keep your skin moisturised
- Avoid using makeup if you notice lesions
- Use sunscreen regularly
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fibre, vitamins, minerals and proteins to keep your skin healthy
Nodules
Nodules are grade-3 to grade-4 acne, characterised by large, inflamed lesions underneath the skin’s surface. They don’t have a visible head. Nodular acne occurs on the face, neck, back, chest, and shoulders and may result in dark spots or scarring.
Causes
Nodules form when the acne-causing bacteria Propionibacterium develops inside the pores and infects them, resulting in swelling from underneath. They are a severe form of acne and take time to heal. Other triggers include hormonal imbalance, side effects of medications, genetics, and exposure to environmental factors.
Symptoms
- Deeply seated bumps underneath the skin
- Accompanied by redness and inflammation
- Have a tough texture
- Painful and irritating
Treatments
For fewer nodules, the dermatologist may prescribe OTC medication and oral antibiotics as the first line of treatment. The doctors may recommend advanced acne treatments such as chemical peels, laser, acne extraction, laser therapy, light therapy, acne draining, and direct medicine injections to reduce the bacteria infection and control inflammation.
Prevention
- Follow a proper skincare routine
- Keep the affected area clean by washing it twice daily
- Use a non-abrasive cleanser for your face
- Do not scrub
- Keep your skin moisturised
- Apply SPF sunscreen every day
- Avoid touching your skin
Cysts
Cystic acne is one of the most severe grades of acne. It appears as a large, pus-filled, and painful inflammation. When left untreated or not treated properly, it can lead to scarring. The most prominent area affected by cystic acne is the face, especially the cheeks, chin, and jawline. Cysts can also occur on other areas of the body, like the upper arms, back, and torso.
Causes
Cysts occur when sebum, dead skin cells and bacteria clog the skin pores, resulting in swelling and redness. The infection seeps into the skin’s surface while damaging healthy tissue, taking several months to heal. Genetics, hormonal changes, stress, and side effects of medications also result in cystic acne.
Symptoms
- Large, pus-filled cysts under the skin
- Painful and tender to the touch
- Inflammation and redness
- When burst, they infect the surrounding skin
Treatments
Cysts or cystic acne can be challenging to treat. Treatment usually involves a combination of treatments, including intralesional injections, chemical peels, and OTC medications. For cystic acne caused due to hormonal fluctuations, the dermatologist may prescribe oral contraceptives. They may also recommend laser treatment to reduce post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and alleviate the scars caused by acne.
Prevention
- Cleanse your skin thoroughly twice a day using a mild cleanser and lukewarm water
- Use oil-free and non-comedogenic skincare products on the skin
- Avoid picking or touching the cysts
- Maintain your hair hygiene
How To Identify Your Acne?
The signs of acne can vary depending on its severity. Broadly, you can categorise acne into mild, moderate and severe cases. Identifying acne involves understanding the different types, their characteristics, and potential causes. The information mentioned above will help you identify your acne. Accordingly, one can distinguish the type and seek medical intervention for prompt treatment.
When To Visit A Dermatologist?
Some acne may go away on their own, but others could be stubborn and require dedicated treatment. If the acne is persistent or recurring and does not show significant change after using OTC products, it is advisable to visit a dermatologist. Acne, when left untreated, can lead to permanent scars. Consult a dermatologist if you find it challenging to manage acne. Speak to your dermatologist if your acne is:
- Filled with pus and getting bigger
- Bleeding
- Resulting in acne flare-ups covering other parts of the body
- Affecting sensitive areas like the eyes and lips
Takeaway
Acne affects people of all ages and may occur for more than one reason. If your acne does not reduce or resolve with OTC treatment, it is best to consult an expert. The dermatologist will help identify the type, severity and underlying cause and recommend a suitable treatment solution customised to your type.