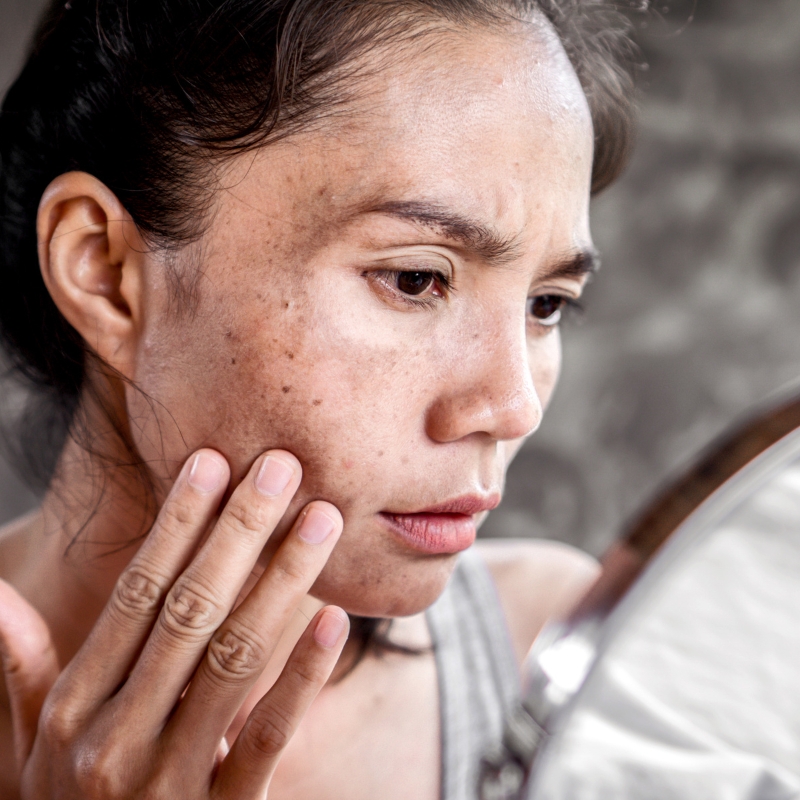
Top 10 Reasons For Pigmentation On Face: Know Its Treatments & Tips
Pigmentation on the face is a common skin concern that affects many people. Pigmentation on face refers to the discoloration of the facial skin, resulting in dark patches or spots. Understanding the reasons behind facial pigmentation can help in finding effective treatments and maintaining healthy skin.
What is Pigmentation?
Pigmentation is the discoloration of the skin caused by melanin, a pigment produced by cells called melanocytes. When the skin produces more melanin than usual, it results in hyperpigmentation, where certain areas of the skin appear darker than the rest. Hyperpigmentation can appear as small or large patches, spots and in some cases even cover the entire body.
Reasons For Pigmentation On The Face
Understanding the underlying causes of pigmentation on the face is essential for effective prevention and treatment.
Here, are the common reasons why pigmentation occurs on the face:
Sun Exposure:
One of the primary causes of pigmentation on the face is sun exposure. The sun emits ultraviolet (UV) rays, specifically UVA and UVB rays, which penetrate the skin and stimulate melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin. Melanin is the pigment that gives skin its color. When the skin is exposed to UV rays, melanocytes increase melanin production as a protective response to absorb and dissipate UV radiation. This leads to the formation of sunspots (solar lentigines) and freckles. Sunspots are flat, brown patches that appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, hands, shoulders, and arms due to prolonged sun exposure. Freckles are small, brown spots that appear primarily on fair-skinned individuals and tend to darken with more sun exposure.
Hormonal Changes:
Hormonal fluctuations are another significant reason for pigmentation of the face. Particularly in women, these hormonal changes can lead to increased melanin production. This is often seen during pregnancy, with the use of oral contraceptives, and during menopause. Hormonal changes stimulate melanocytes to produce more melanin, resulting in melasma. Melasma, also known as “the mask of pregnancy,” presents as brown or gray-brown patches primarily on the face, affecting areas such as the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip.
Skin Injuries and Inflammation:
Skin injuries and inflammation are common causes of pigmentation on the face. When the skin undergoes injury or inflammation, such as cuts, burns, acne, or eczema, it can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). The skin responds to injury by producing more melanin in the affected area during the healing process. PIH appears as dark spots or patches where the skin was previously injured or inflamed. This condition is more common in individuals with darker skin tones, where the skin’s natural response to injury involves increased melanin production.
Genetic Factors:
Genetic factors play a significant role in the pigmentation of the face. Genetics determine how much melanin your skin produces. Some people are naturally predisposed to higher melanin production, leading to conditions like freckles and other forms of pigmentation. Freckles are small, brown spots that typically appear on the face, neck, and arms. They are hereditary and become more prominent with sun exposure.
Medications:
Certain medications can be a cause of pigmentation on the face. These medications may sensitize the skin to sunlight or directly stimulate melanocytes. Drug-induced hyperpigmentation can occur with medications such as chemotherapy drugs, certain antibiotics, and antimalarial drugs, leading to pigmentation changes.
Medical Conditions:
Some underlying medical conditions are reasons for pigmentation on the face. These conditions may affect hormone levels, melanin production, or skin healing processes. For instance, Addison’s disease affects the adrenal glands and can lead to increased melanin production, resulting in darkening of the skin. Hemochromatosis, a genetic disorder causing the body to absorb too much iron, can deposit in the skin and cause pigmentation changes.
Types of Facial Pigmentation
- Melasma: This type of pigmentation is characterized by brown or gray-brown patches, commonly seen on the face, especially on the cheeks, forehead, and upper lip. It is often caused by hormonal changes, such as pregnancy or birth control pills.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines): Also known as age spots or liver spots, these are flat, brown spots that appear on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, hands, and arms. They result from prolonged sun exposure.
- Freckles: Small, brown spots that appear on sun-exposed areas of the skin, primarily on fair-skinned individuals. They are genetic and tend to become darker with sun exposure.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs when the skin darkens after an injury or inflammation, such as acne, eczema, or cuts. It is more common in people with darker skin tones.
How to Prevent Pigmentation On Face?
-
Sun Protection:
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen on entire face and neck area with an SPF of 30 or higher every day, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours and wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses.
-
Avoid Peak Sun Hours:
Limit sun exposure, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when UV rays are the strongest.
-
Regular Skincare Routine:
Incorporate products with ingredients like vitamin C, niacinamide, and licorice extract, which can help lighten pigmentation.
-
Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can promote healthy skin and prevent pigmentation on face.
Effective Treatments for Pigmentation on Face
Dealing with facial pigmentation can be challenging, but there are several effective treatments available to help reduce and manage pigmentation on the face. Here are some of the top options:
Topical Treatments
Over-the-counter creams and prescription medications containing ingredients like hydroquinone, retinoids, and corticosteroids can help lighten dark spots caused by pigmentation on the face.
Chemical Peels
A dermatologist can perform chemical peels using acids to exfoliate the skin, removing the top layer and reducing facial pigmentation. This treatment helps in rejuvenating the skin and diminishing pigmentation from the face.
Laser Therapy
Laser treatments target and break down melanin in the skin, effectively reducing pigmentation from the face. This advanced treatment can significantly improve the appearance of pigmented areas.
Microdermabrasion
This procedure exfoliates the skin using fine crystals, helping to reduce the appearance of pigmentation on the face. Microdermabrasion promotes new skin growth, leading to a more even skin tone.
Home Remedies
Natural ingredients like aloe vera, green tea extract, and turmeric have anti-inflammatory and skin-lightening properties that can help with pigmentation on the face. These home remedies for pigmentation on the face can be an excellent addition to your skincare routine for managing it.
By exploring above treatment options, you can effectively manage and reduce pigmentation on your face, achieving a clearer and more even complexion.
Frequently Asked Questions On Pigmentation On Face:
Q1: Can pigmentation be completely cured?
A1: While pigmentation can be significantly reduced, it may not be completely cured. Consistent treatment and sun protection are key to managing pigmentation.
Q2: Are natural remedies effective for pigmentation?
A2: Natural remedies can help lighten pigmentation to some extent, but they are usually less effective than medical treatments. Consult a dermatologist for the best results.
Q3: How long does it take to see results from pigmentation treatments?
A3: The time to see results of pigmentation varies depending on the treatment and the severity of the condition. Topical treatments may take several weeks, while professional procedures like laser therapy can show quicker results.
Q4: How to Remove Pigmentation from Face Permanently?
A4: Medical treatments such as laser therapy and chemical peels helps to remove pigmentation permanently. These treatments target and break down excess melanin in your skin, effectively reducing pigmentation with long-lasting results.
Q5: What is Pigmentation on the Face?
A5: Pigmentation on the face refers to the discolouration of facial skin, resulting in dark spots or patches. This condition occurs because melanocytes overproduce melanin, which can trigger various factors like sun exposure, hormonal changes, and skin injuries.
Q6: How to Remove Pigmentation from Face Permanently at Home?
A6: Permanently removing pigmentation at home is challenging, but consistent use of topical treatments containing vitamin C, retinoids, and alpha hydroxy acids can help lighten pigmentation on the face. These ingredients exfoliate your skin, promote cell turnover, and inhibit melanin production, gradually reducing pigmentation.
Q7: What is the Best Diet for Pigmentation on the Face?
A7: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals can help you reduce pigmentation. Foods like fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds provide essential nutrients that promote skin health and reduce oxidative stress, helping you manage facial pigmentation.
Q8: How to Treat Pigmentation on the Face?
A8: One can treat pigmentation on the face with topical treatments, medical procedures, and sun protection. Effective treatments include creams with hydroquinone or retinoids, chemical peels, laser therapy, and consistent use of sunscreen to prevent further pigmentation.
Q9: What Causes Pigmentation on the Face?
A9: Sun exposure, hormonal changes, skin injuries, genetic factors, medications, and certain medical conditions can cause pigmentation on the face. These factors stimulate melanocytes to produce excess melanin, leading to the appearance of dark spots and patches on your skin.
Takeaway
Pigmentation on the face can be a frustrating issue, but understanding its causes and types can help in finding effective treatments. Prevention through sun protection and a healthy skincare routine is crucial. If you’re struggling with pigmentation, consult a dermatologist to determine the best course of action for your skin type and condition. By following these guidelines and taking proactive steps, you can achieve a more even and radiant complexion.
Our certified subject matter experts do extensive research and collate facts from reputed scientific journals and international studies to create informative and engaging articles related to all your dermatology concerns. They strive to help you decipher medical jargon, distinguish fact from fiction and overcome paranoia. Our qualified medical board or expert panel goes a step further to verify these facts based on their rich academic knowledge, vast clinical experience and critical industry insights to ensure you consume only medically accurate content that empowers you to make informed decisions about your hair and skin-care treatments and weight management. Check out our Editorial policy for further details
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9165630/https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10304091/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4142815/
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323808
https://www.health.harvard.edu/diseases-and-conditions/demystifying-hyperpigmentation-causes-types-and-effective-treatments