What Is Acne Keloidalis Nuchae And How To Treat It?
Acne keloidalis nuchae(AKN) is often confused with acne vulgaris because of the presence of the word ‘acne’ in its name. This skin condition is not related to your ‘run of the mill’ pimples and is often a major concern for people affected by it. This is because of the extensive scarring it can cause in prominent areas such as the nape of the neck.
What Is Acne Keloidalis Nuchae?
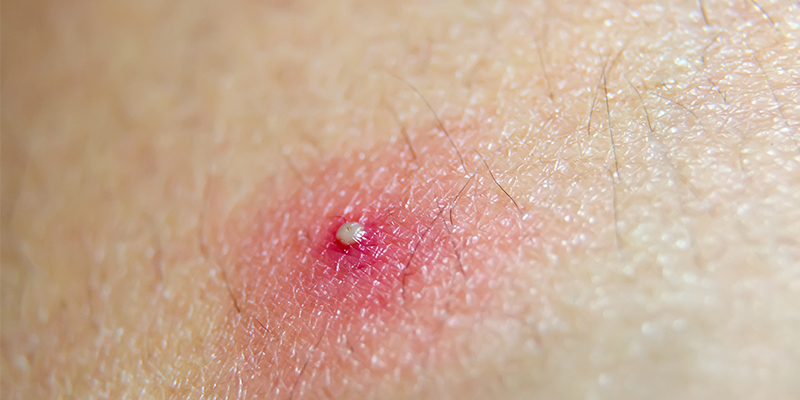
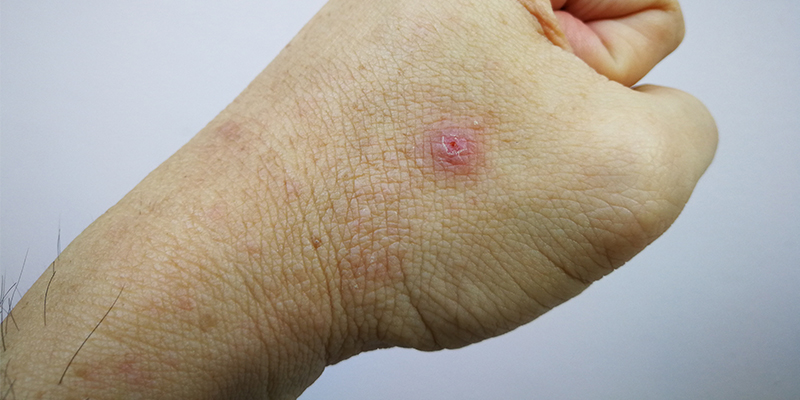
When the hair follicles in the skin are inflamed for prolonged periods of time, papules and pustules form. These start as itchy bumps but then get filled with pus which are painful too. The result of this chronic inflammation is acne keloidalis nuchae, which is a benign skin condition characterized by inflamed follicles in the form of papules and pustules primarily in the head and neck regions. These lesions resemble keloid scars (raised scars on the skin).
Acne keloidalis nuchae is also known as acne cheloidalis nuchae, folliculitis keloidalis, dermatitis papillaris capillitii or sycosis framboesiformis.
Who Gets Acne Keloidalis Nuchae?
Men and women in the age group of 10 years to 25 years are mostly affected by Acne keloidalis nuchae. It is very rarely seen in adults above the age of 25 years. The predominance of this skin condition is higher in males than in females. It has been observed that people who are dark skinned are most affected by it.
Must Read: What Is The Best Acne Treatment For Teenage Boys?
What Causes Acne Keloidalis Nuchae?
This skin condition is caused because the affected hair follicles which are chronically inflamed and get infected eventually. It is also important to note that Acne keloidalis nuchae is not a contagious skin condition. While causes of this conditions are not clear, there are certain elements or habits that have been known to increase the chances of the individuals developing acne keloidalis nuchae. These include –
- Wearing tight clothes such as sporting gear that increase the friction generated between the skin and the clothing material.
- Shaving too closely causes chronic trauma on the skin
- Obesity
- Certain medications
- Metabolic conditions
What Are The Common Signs And Symptoms?
- Presence of papules and pustules
- Skin lesions which look similar to keloid scars
- Intense itching or scratching at the affected site
- Painful cysts
- Red bumps that are often filled with pus
- Head and neck regions are mostly affected but the skin lesions may also develop on other areas of the body
- Scarring from this skin condition can lead to hair loss eventually.
Must Read: What Is The Best Way To Clear Acne?
How Is Acne Keloidalis Nuchae Diagnosed?
For appropriate diagnosis of acne keloidalis nuchae, book an appointment with an experienced dermatologist. It is vital that this skin condition is identified accurately and not mistaken for acne vulgaris. The dermatologist may conduct the following examinations as part of the diagnosis –
- A physical examination of the affected skin (naked eye, dermoscope, Wood lamp’s examination, etc.)
- A review of the medical history of pimples and related skin conditions, autoimmune conditions, etc.
- A review of the medications that you are taking or have taken in the past six months
- Complete blood count (CBC) to analyse any underlying conditions
- A skin biopsy for thorough diagnosis
- A differential diagnosis with acne vulgaris and other types of pimples may also be conducted.
Possible Complications
The presence of papules and pustules is embarrassing in social situations and can cause emotional stress to the person experiencing this skin condition. Physically, the possible complications of Acne keloidalis nuchae are –
- The intense scratching can cause secondary skin infections
- Abscess formations due to infection
- Permanent scars that are deep
- Hypopigmentation or hyperpigmentation at the affected site
Must Read: How To Remove Blemishes On Face?
Acne Keloidalis Nuchae Treatment
Acne keloidalis nuchae treatment in India is directed by the severity of the condition. Some of its treatments include:
- Intralesional Injections – In some cases, injection containing triamcinolone or corticosteroids may be given at the site of the inflamed skin lesions. Such injections are often used in the treatment of keloid scars to lower the raised surface of the scar.
- Laser Therapy – Laser ablation of the skin to remove the top damaged skin layers can be performed using certain wavelengths and types of laser light. These lasers are proved to be safe for usage on the facial skin and even the other areas of the body. The energy from the laser efficiently exfoliates the skin and causes micro-wounds to form. As these wounds heal, the prior acne and acne scars heal to reveal fresher looking, rejuvenated and flawless skin. The heat energy from the laser promotes collagen production in the skin and hence, aids in faster and better recovery of the skin cells.
- Topical Medications – Mild versions of the skin issues can often be brought under control by using antimicrobial agents, benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, anti-inflammatory creams, etc.
- Topical Retinoids – For mild to medium severity, the dermatologist may prescribe topical retinoids to bring the itching and inflammation under control. This will eventually help the skin lesions to heal faster.
- Oral Medications – In combination with topical treatments, oral medications such as isotretinoin and antibiotics (for example, tetracycline) may be prescribed by a skin specialist. These will help with controlling the inflammation from within, reducing keratinization and dealing with the infection causing bacteria.
- PUVA Treatment – This treatment utilizes ultraviolet radiation to bring down the inflammation and also to treat the infection to a certain extent. The skin affected with acne keloidalis nuchae is subjected to UV radiations of a certain wavelength for a specific period of time. The skin is subjected to this exposure in an extremely controlled environment in order to avoid any side effects that are related to UV exposure.
- Surgical Excision – If all the above methods seem to be unfruitful in getting rid of acne keloidalis nuchae, dermatologists and cosmetic surgeons may suggest to opt for surgically removing the lesion so that the scar left behind is evidently minor and less noticeable than the one the pustule/papule would leave behind on the skin. Local anesthesia is used to numb the skin and avoid any discomfort during the procedure.
Must Read: Do Antibiotics Help To Treat Acne Safely?
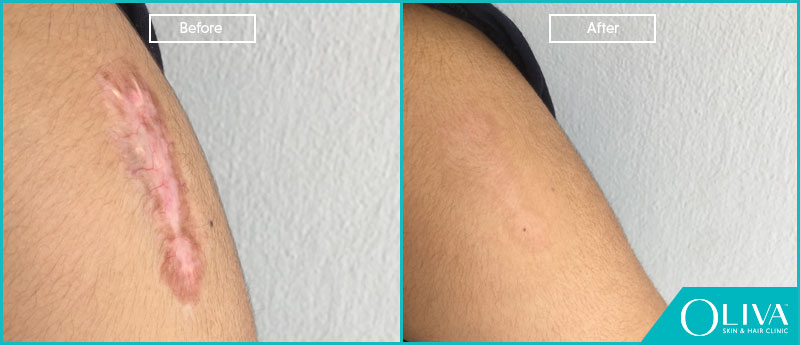
Before And After Results
How To Prevent Acne Keloidalis Nuchae?
- Maintain personal hygiene and wash your face and neck twice a day. Do not wash too often.
- Use a cleanser and moisturizer that is meant for your skin type, so that you can avoid unnecessary build up of oils on the skin that can clog the pores.
- Avoid shaving too closely and use a shaving gel at all times.
- Wear collarless tops, shirts or jackets to minimize the friction around the neck region.
- Whenever possible, avoid wearing hats as they can create friction at the back of the head and neck.
- Do not touch or pop acne, no matter where they crop up on your body. Popping them can lead to infection and scarring.
- Use a gentle scrub (preferably recommended by a dermatologist) to keep dead skin cells build up at bay.
- Avoid harsh soaps or cleansers for not just your face but also for the rest of the body.
- Do not use hair styling gels or creams too often as they can plug the hair follicles easily.
- Eat a healthy diet and exercise regularly to optimize blood circulation and promote rejuvenation of skin cells.
Must Read: How Can You Get A Pimple Free Face – Skin Tips From Dermatologist
Prognosis For Acne Keloidalis Nuchae
This skin condition usually has a good prognosis when treatment is started on time and is in accordance with the severity of the condition. If the skin lesions (acne cysts) have progressed into deeper layers of the skin, the prognosis can alter with permanent scars forming on the skin. However, these scars can also be treated in time with laser therapy.
Acne keloidalis nuchae is a chronic form of folliculitis that often presents itself in the form of pus-filled bumps that develop into keloid-like scars in the head and neck regions. A definitive diagnosis along with a differential diagnosis can help to identify this skin condition precisely. A systematic treatment plan devised after thorough examination and analysis by a dermatologist can help you treat this skin condition without having to worry about any remnant scarring.